Describe the Energy and Motion of Particles in a Solid.
The temperature of a substance is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles. Consider a pure rotation of a solid object.

Particle Model Specific Latent Heat Internal Energy State Changes Gas Pressure Cooling Heating Curve Investigations Experiments Igcse O Level Gcse Physics Revision Notes
Liquids and solids are often referred to as condensed phases because the particles are very close together.

. In the physics of solids surfaces must be intrinsically less energetically favorable than the bulk of a material the molecules on the surface have more energy compared with the molecules in the bulk of the material otherwise. States of Matter - PhET Interactive Simulations. Basics 1121 - PhET Interactive Simulations.
Conservation laws for systems of particles In this chapter we shall introduce but not in this order the following general concepts. Whats matterNo no no not whats THE matter. Solid rocks for example can be formed by the cooling of molten rock the accumulation and consolidation of sediments or the alteration of older rocks by heat pressure and fluids.
Here the authors report. In this episode of Crash Course Kids Sabrina talks about what matter is and the three s. A rotating object has kinetic energy because all particles in the object are in motion.
The work done by a force. Solid vibrate jiggle but generally do not move from place to place. Sound waves carry energy through the.
As molten rock cools and solidifies particles within the rocks align. The waves on your jump rope transport energy but the particles in the jump rope itself stay put. The units of moment of inertia are kg m2.
Nature Energy - Intensive research is underway to develop solid-state electrolytes for rechargeable batteries. Describe how energy must change in order to make the following phase changes. Molecules in the solid phase have the least amount of energy while gas particles have the greatest amount of energy.
The motion of plates can be described in four general patterns. Thermal energy is the random motion of particles whether vibrations in solid matter or molecules or free motion in a gas this energy is distributed among all the particles in a system through collisions and interactions at a distance. It is composed of two distinctly different types of material.
In solid steel the particles have less energy and are moving slower than in liquid steel. The angular impulse of a force. A change in phase may occur when the energy of the particles is changed.
We should probably ask first about the motion of a particle in a uniform electric field. Recall that the crust is the solid rocky outer shell of the planet. Matter at any temperature above absolute zero contains thermal energy.
The total energy of a system can be subdivided and classified into potential energy kinetic energy or combinations of the two in various ways. The power transmitted by a force. Where does the energy from the inside of the stainless steel freezer of science.
The linear impulse of a force. Kinetic energy is determined by the movement of an object or the composite motion of the components of an object and potential energy reflects the potential of an object to have motion and generally is a function. The potential energy of a force.
The following table summarizes properties of gases liquids and solids and identifies the microscopic behavior responsible for each property. However if the particle picks up enough energy to become relativistic then the motion gets more complicated. The less-dense continental crust and the more-dense oceanic crust.
Translational Kinetic Energy m I v Moment of inertia is the rotational equivalent of mass. The linear momentum of a particle or system of particles. Liquid gas ___ energy is added _____ Liquid solid ___ energy is taken away ____ 8.
Surface free energy or interfacial free energy or surface energy quantifies the disruption of intermolecular bonds that occurs when a surface is created. Transfers of energy and the movements of matter can cause chemical and physical changes among Earths materials and living organisms. At low velocities the motion is not particularly interestingit is just a uniform acceleration in the direction of the field.
There are spaces between particles of matter. The kinetic energy due to rotation is called rotational kinetic energy.

Particle Theory Changes Of State

The Kinetic Theory Of Matter Matter Science Kinetic Theory States Of Matter

This Diagram Shows That As Energy Is Added To Matter In The Form Of Heat Solids Become Liquids And Liqui States Of Matter Kinetic Theory Properties Of Matter
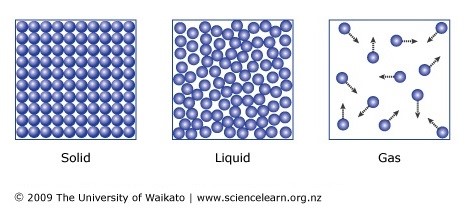
5 10 Describe The Arrangement And Motion Of Particles In Solids Liquids And Gases Tutormyself Chemistry
No comments for "Describe the Energy and Motion of Particles in a Solid."
Post a Comment